Micron demonstrated its massive 256 GB MCR DIMM memory modules this week at the Nvidia-hosted GPU Technology Conference (GTC). These modules are designed for next-generation servers, including those running Intel’s Xeon Scalable ‘Granite Rapids’ processors. Micron announced earlier this week that the new 256 GB MCRDIMMs are currently being sampled with its customers.
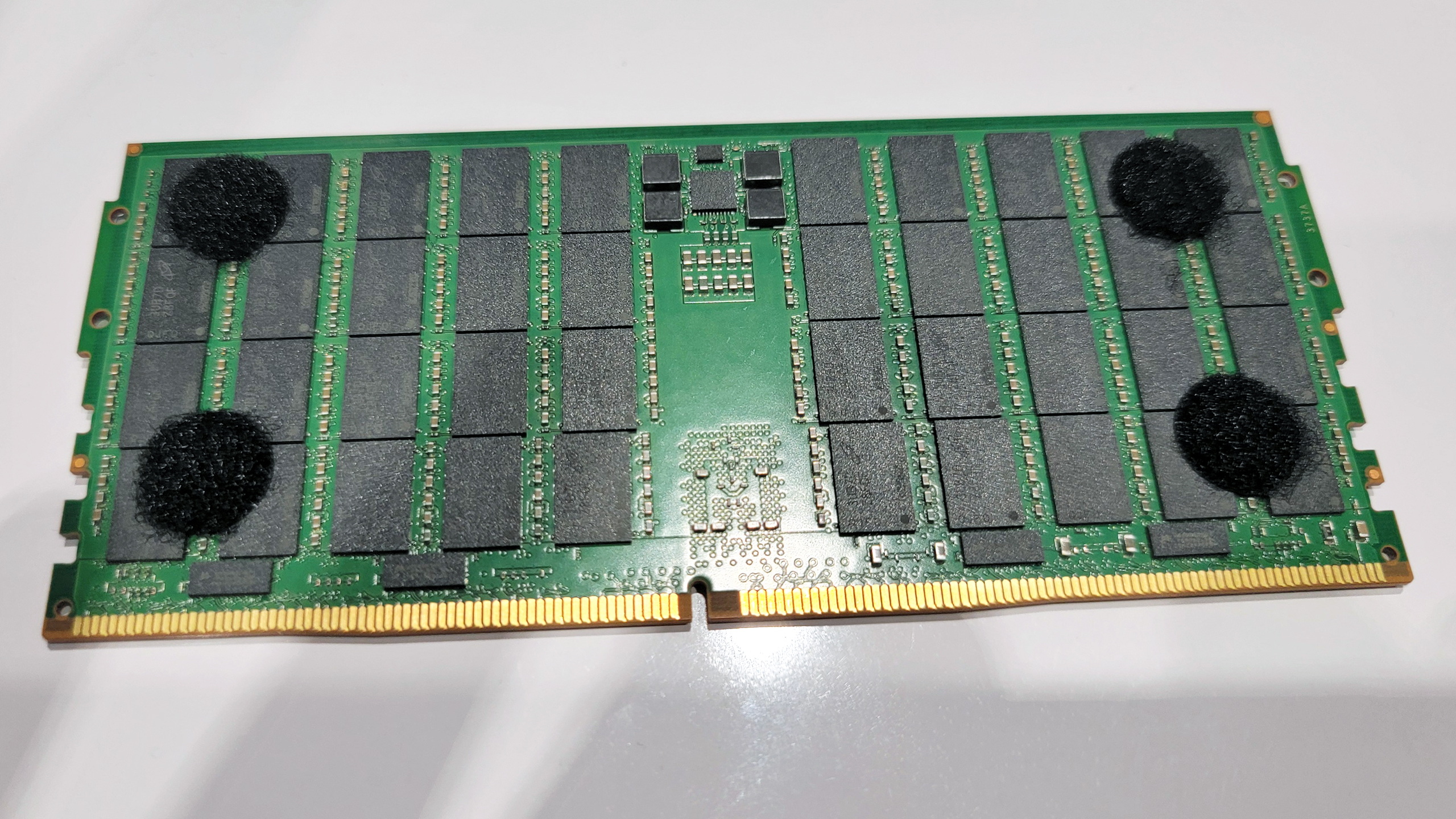
Micron demonstrated one ‘tall’ 256 GB DDR5-8800 MCRDIMM at GTC (pictured) but also plans to offer MCRDIMMs of standard height for applications like 1U servers. Both 256 GB MCRDIMMs are based on monolithic 32 Gb DDR5 ICs, but the tall one places 80 DRAM chips on both sides of the module, whereas the standard one uses 2Hi stacked packages, which means that they run slightly hotter due to less space for thermal dissipation. In any case, the tall module consumes around 20W, which isn’t bad as Micron’s 128GB DDR5-8000 RDIMM consumes 10W at DDR5-4800.

Multiplexer Combined Ranks (MCR) DIMMs are a type of dual-rank memory module that enables both ranks to operate concurrently using a specialized buffer. The buffer allows the two physical ranks to act as if they were two separate modules working in parallel, thereby doubling performance by enabling the simultaneous retrieval of 128 bytes of data from both ranks per clock, effectively doubling the performance of a single module. Meanwhile, the buffer works with its host memory controller using the DDR5 protocol, albeit at speeds beyond those specified by the standard, at 8800 MT/s in this case.
Typically, modules with two physical ranks function as a single module, meaning that when the host CPU (or memory controller) retrieves data from such a module, it is limited to fetching 64 bytes of data at a time. MCRDIMMs double that, thus substantially increasing per-module capacity and performance.
Considering the fact that Micron demonstrated its 256 GB MCRDIMMs at Nvidia-hosted GTC, it is likely that the company positions these products for AI servers based on Intel’s Xeon Scalable ‘Granite Rapid’ processors. Since such machines tend to require a huge amount of memory for training, the new high-capacity modules will come in handy. Intel’s Xeon Scalable ‘Granite Rapid’ CPUs have a 12-channel memory subsystem supporting two modules per channel. Using Micron’s 256 GB MCRDIMMs, a Granite Rapid-based machine can accommodate 3 TB of DDR5 memory using 12 slots and 6 TB of DRAM using 24 slots.