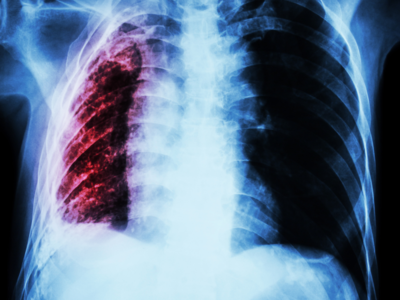
After COVID – 19, the World Health Organisation has now announced Tuberculosis as the top infectious disease that has caused numerous deaths in 2023. A report published by WHO on Tuesday has highlighted the challenges the world countries have faced in eradicating the disease.
The report claimed that about 8.2 million people were diagnosed in 2023 with Tuberculosis and it caused 1.23 million deaths. Though there is enough medication for people, it is still a disease that is far distant from being eradicated. According to the UN report, it is alleged that there is underfunding for the research and that they are not able to find the cure and eradicate the disease. The report also mentioned that it is a “distant goal.”
(Image: Canva)
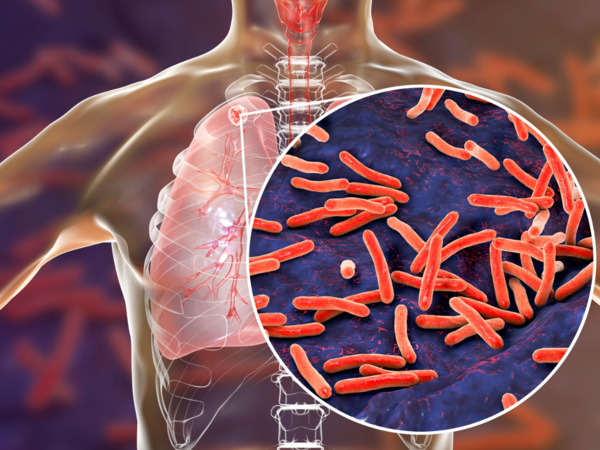
The WHO report also mentioned that 2023 reported the highest figure of Tuberculosis since it kept track of the infection from 1995.
Tuberculosis in highly populated countries
When compared to the developed countries, TB has affected the most in the 30 countries that are highly populated with India being the highest by 26%. Followed by Indonesia, China, Philippines and Pakistan.
(Image: Canva)
WHO director general, DR Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, said,“WHO urges all countries to make good on the concrete commitments they have made to expand the use of those tools, and to end TB.”
Why TB is a top killer?
In the past 2 years, Tuberculosis has become a high risk factor because it is highly contagious.TB spreads through air from an infected person through cough or sneeze and even in cases when they speak. It is easy to transmit and TB remains dormant in a human body for years even without showing any symptoms. TB also weakens the immune system of people who have HIV, malnutrition or other underlying health conditions.
(Image: Canva)
Risk factors for TB
Multiple new cases in TB have been driven by various risk factors that include undernutrition, HIV infection, alcohol use disorder, smoking, diabetes among others. As TB is resistant to antibiotics, it is very hard to treat and the drugs TB (MDR-TB) and TB (XDR-TB) were made to cure, but difficult to stop spreading.
Symptoms of Tuberculosis
1. Persistent cough
The cough pertains for more than three weeks and it leads to producing thick mucus mixed with blood.
2. Chest pain
It develops chest pain when coughing.
3. Fever
The TB causes chills in patients along with fever
4. Night sweats
It causes a person to randomly sweat in excess especially at night.
5. Fatigue and weight loss
TB leads to loss of appetite, sudden weight loss and make the body tired and weak at all times.
(Image: Canva)
TB usually affects the lungs but in certain cases, which is extrapulmonary TB, the disease affects the spine, kidneys and even brain of the human.
Why has Tuberculosis become worse than COVID 19?
When compared to COVID, TB takes a lot of time, sometimes even a month for the symptom to appear. It makes it very difficult to find an underlying disease and it becomes late to isolate the infected person before it transmits to many others. The incubation period for it is also high TB is one of the diseases that require a long and complex course of treatment. The infection stays for more than six months.
Tuberculosis has also become a major global health problem with millions of people infected each year. While COVID-19 had a significant impact, it took less than a year to find a cure and a way to contain the infection to a particular area. It is important to note that both TB and COVID-19 are deadly diseases that take life, but medication for TB is still not enough.





