Stealing personal data has become such a lucrative crime. Swiping passwords and other credentials allow criminals to break into victims’ apps allowing these cybercrooks to wipe out financial accounts via banking and trading apps. This information can also lead to more sophisticated crimes using SIM swaps and identity thefts. The latest news from Cybernews is downright frightening as a record 16 billion login credentials have been exposed.
Information stolen in the breach included credentials from online services connected to Apple, Facebook, Google, GitHub, and Telegram. Data from users of various government services was also made public. Researchers say that this data can be used to drive phishing campaigns, power attacks created to take over online accounts, generate ransomware attacks, and more.
One dataset with 455 million records was named to indicate that it originated with the Russian Federation. One with 60 million records was named after the cloud-based Telegram messaging service. At this point, it is unknown who owns the leaked data although it would appear that at least some of the massive collection of data came from cyber criminals.
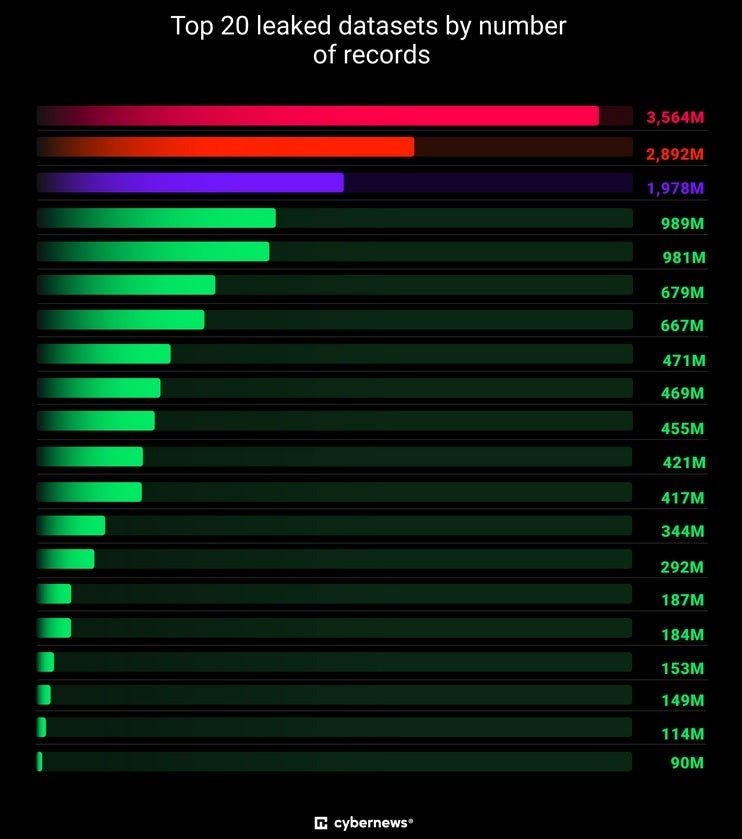

Top 020 leaked datasets from the theft of 16 billion login credentials. | Image credit-Cybernews
Researchers say that most of the data exposed in the breach “is a mix of details from stealer malware, credential stuffing sets, and repackaged leaks.” Since there were overlapping records, it is impossible to determine exactly how many individuals were impacted by the data breach. Having said that, the stolen data follows a particular order with the URL first followed by login credentials and then passwords. According to Cybernews, modern infostealers, defined as malicious software stealing sensitive information, collect data in this order verifying that the data collected was stolen.
Here’s the scary part. Even if the attackers who owned the data were able to get login credentials from only 1% of the victims, that would leave over 1 million individuals some of whom could be vulnerable to getting fooled into giving up even more information.
What you should do is change your passwords to strong ones often. Don’t tap on links found in emails or texts; be suspicious. Assume every text or email is a scam and do not give away personal information.







