Synopsis: The GCCs stand out as one of the most significant and powerful forces that have been driving the Indian commercial real estate market in the year 2025. The GCCs hold approximately 40% of the total office space in India.
Currently, India is one of the fastest-growing markets in the global GCC sector, capitalizing on their strong talent bases, cost competitiveness, and conducive government policies, and building a robust ecosystem in technology, finance, life sciences, and engineering services. This trend has significantly impacted India’s office property market, giving a major push to large office spaces, hybrid working, and flexible workspaces that continuously emphasize agility and scalability.
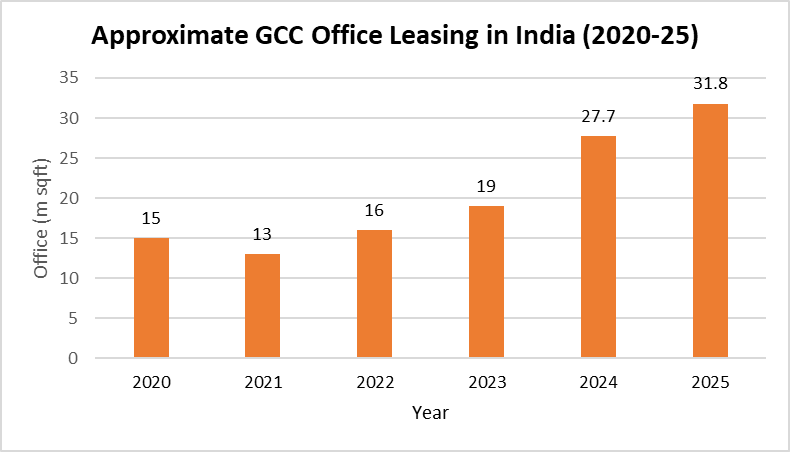
Impact on office space driven by GCCs
The size of the Indian commercial realty market, pegged on economic activity, ranking fourth largest in the world with a value of $50-60 billion, is set to touch $120-130 billion by 2030. The GCCs’ hubs are likely to develop 160 – 200 million sq. ft. of office space by 2030. Today, India hosts over 1,850 GCCs, employing 2.2 million professionals.
- The Indian flexible office space market offers a contribution of 65-80 million sq. ft. that may likely reach $9-10 billion in the year 2028.
- The focus of demand is on high-end, ‘tech-ready’ properties, smart properties, large floor plate properties, and those with robust ESG.
- GCCs are also propelling significant leasing, mostly in the tech hub of Bengaluru, Hyderabad, and Chennai, and extending to Tier 2 cities.
- Offices are turning out to be innovation hubs with areas that allow both work and play in order to entice talent.
- Visakhapatnam, Coimbatore are emerging as the GCCs are balancing talent availability and cost with the use of satellite offices.
India as a GCC Hub in Various Cities
Expansion of the GCC has stopped being in metro regions such as Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Mumbai, Chennai, or even Pune. New regions come up in the form of Coimbatore, Kochi, or even in Jaipur and Ahmedabad, where the support of talent, property affordability, and low employee attrition make the regions attractive. It results in quicker occupation of Grade A office spaces, development of infrastructure, and the development of business districts. The states are offering quicker approval, technology zones, and operational campus spaces to the industry. Mid-tier IT companies need plug-and-play offices. Tier 2 or Tier 3 cities account for a projection of 13-15% in hiring.
Supporting schemes that are boosting GCC in India
It has strong policy tailwinds propelling it forward. Schemes like Modified Electronics Manufacturing Clusters (GENISIS) innovation schemes, skills for the digital age under FutureSkill Prime, and easing of clearances through ease of business initiatives at the state and center level governments are enabling global companies to grow quickly in these areas. It has easier FDI policies, and SEZ policies that are favorable for the entry and growth of GCCs. In India, GCCs have grown from being mere back offices for administration, finance, human resources, and other support functions for companies, to being strategic innovation centers for engineering R&D, particularly for Aerospace, Defense, Semiconductors, and Advanced Manufacturing.
India’s GCC city-level dynamics
Hyderabad is emerging as a hub for GCCs in addition to mid-sized companies in their search for a cost-effective location. Netflix, Eli Lilly, Costco, and McDonald’s have set up operations in Hyderabad, with over 70 GCCs, along with the other large French beauty company L’Oreal. Bangalore is the pioneer focusing on deep tech, AI, R&D, digital manufacturing, attracting huge investments and talent. Delhi is also a multi-sector powerhouse with strong capabilities in BFSI consulting and technology. Chennai & Pune also concentrated on engineering, manufacturing, and BFSI. Tier 2 cities – Indore, Bhubaneswar, Vizag, Kochi – are increasing fast because of cost reasons 20-30% lower OPEX and talent attraction by players like Cognizant. Tier 1 cities showed 86 – 87% implied recruitment demand,
Investment Trends Analysis:
- The GCCs are transforming into innovation hubs in AI, ML, Cybersecurity, and sustainability.
- KKR, Blackstone: Private Equity firms force portfolio firms to open GCCs in India
- Some of the upcoming companies in the market are Dai-ichi Life, Jaggaer, eBay, and Ferguson.
- The sector of the GCCs is anticipated to reach $100 billion with the presence of 2200+ GCCs in the market by 2030.
Also read: Upcoming Hotspots: GCC Demand in Tier-2 Cities Set to Grow by 30–40% by 2028
GCC leasing potential in India: 2025 – 2030
The estimated GCC Leasing in India is 120-246 million sq ft, based on global business conditions. The sectors that GCCs are leasing space to include 16% in Automotive, 9% in Life Sciences, and 5% in semiconductors. As per a report by Savills in 2020-24, there is 77% of leased area in Bengaluru, Hyderabad, and Pune in IT-BPM, while in BFSI, it is 64% in Mumbai, Pune, and Hyderabad, followed by 78% in engineering, manufacturing, and cities like Bengaluru, Pune, and Chennai, and finally, 86% in Healthcare & Pharma in Hyderabad, Bengaluru, and Pune cities.
Hiring Rebounds
GCCs provide an average compensation rate that is 12-20% higher than that offered by regular technology product and service companies as well as non-technology companies indirectly hiring technology talent. The expansion of growth driven by GCCs contributes to roughly 27% of the overall requirement measure as the hiring in the Information Technology services sector continues to be modest and highly selective. For the year 2026, the overall hiring in the Information Technology sector will increase by a measure of 12-15% led by the expansion of GCC and AI First Cloud and Cyber initiatives.
GCC vs IT Service Companies hiring
| Segment | GCCs | Information Technology Services & Consulting |
| 2024 share trend | 15 % Demand approx. | Modest 7-8% growth over 2023 |
| 2025 share/trend | Fastest growing segment with 27% in demand | Growth restrained focus on selective skill hiring. |
| 2026 forecast | Remains at the forefront of cremental hiring in digital and engineering. | 6-8% recruitment growth in 2026 no broad pyramid expansion. |
Future Outlook
- Looking ahead, the role of GCCs in shaping the Indian commercial realty market and economic system is only going to accelerate.
- The number of GCC citizens is projected to rise from 1,800+ at present to over 2,400 in 2030.
- This will further accelerate the leasing of offices and real estate. With the rising percentage of office absorption each year, the Gulf Cooperation Countries (GCCs) are forecasted to be the single biggest space occupier in the top office markets of India.
- The market for flexible workspace and hybrid office space is expected to see accelerated demand along with Grade A office spaces as organizations strive for flexibility in workspace strategy and Opex models. Government initiatives and policies to make India an attractive innovation destination would continue to drive demand.
- Skill development strategies, infrastructure, and business facilitation would be critical in shaping policies. Along with increasing costs in the primary destinations, Tier-2 cities are also being recognized as possible winners with lower costs of real estate and development of new GCC points. Many MNCs and Tech companies are providing opportunities for young talent with AI / ML and other skills.
Conclusion
Global Capability Centres have significantly shaped the paradigm of India’s commercial real estate industry. Indian commercial real estate has evolved into a primary drivers of the large-scale leasing of offices and has suddenly emerged as a shaping factors in the demand for flexible working space and a factor of a city’s competitiveness.
Written by Soumya M







